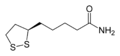
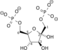
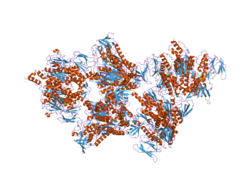二氫硫辛醯胺脫氫酶(EC 1.8.1.4,英語:Dihydrolipoamide dehydrogenase,縮寫DLD,又稱為粒線體二氫硫辛酸脫氫酶,dihydrolipoyl dehydrogenase, mitochondrial)是一種由人類基因DLD[1][2][3][4]所編碼的黃素蛋白,其作用是將二氫硫辛醯胺脫氫從而轉化為氧化型硫辛醯胺。
DLD作為一種粒線體蛋白質,在真核生物的能量代謝中起到重要作用,它至少參與了五種多酶複合體,且為複合體完成反應所必需的組份[5]。另外,DLD作為一種黃素蛋白氧化還原酶,以FAD為輔基接受質子與電子催化二硫鍵的形成。
DLD是大小為51千道爾頓亞基的同二聚體,其中每個亞基都與一分子的FAD以共價鍵的形式相連[6]。
功能
在哺乳動物的粒線體三羧酸循環中,該酶與丙酮酸脫氫酶和二氫硫辛醯基乙醯基轉基酶一起組成中丙酮酸脫氫酶複合體,同時該酶亦是α-酮戊二酸脫氫酶複合體中的一個組分。二氫硫辛醯胺脫氫酶的主要任務是負責將複合物中另一組分硫辛醯胺轉乙醯基酶(或二氫硫辛醯琥珀醯轉移酶)的輔基二氫硫辛醯胺脫氫從而轉化為氧化型硫辛醯胺,該酶也是粒線體甘氨酸剪切體系的組分。
參考文獻
- ↑ Entrez Gene: dihydrolipoamide dehydrogenase.
- ↑ Otulakowski G, Robinson BH. Isolation and sequence determination of cDNA clones for porcine and human lipoamide dehydrogenase. Homology to other disulfide oxidoreductases. J. Biol. Chem.. December 1987, 262 (36): 17313–8. PMID 3693355.
- ↑ Pons G, Raefsky-Estrin C, Carothers DJ, Pepin RA, Javed AA, Jesse BW, Ganapathi MK, Samols D, Patel MS. [http//www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC279783/ Cloning and cDNA sequence of the dihydrolipoamide dehydrogenase component human alpha-ketoacid dehydrogenase complexes]. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A.. March 1988, 85 (5): 1422–6. doi:10.1073/pnas.85.5.1422. PMID 3278312. PMC 279783.
- ↑ Scherer SW, Otulakowski G, Robinson BH, Tsui LC. Localization of the human dihydrolipoamide dehydrogenase gene (DLD) to 7q31----q32. Cytogenet. Cell Genet.. 1991, 56 (3-4): 176–7. doi:10.1159/000133081. PMID 2055113.
- ↑ Babady NE, Pang YP, Elpeleg O, Isaya G. [http//www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC1851069/ Cryptic proteolytic activity of dihydrolipoamide dehydrogenase]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America. 2007, 104 (15): 6158–63. doi:10.1073/pnas.0610618104. PMID 17404228. PMC 1851069.
- ↑ Ciszak EM, Makal A, Hong YS, Vettaikkorumakankauv AK, Korotchkina LG, Patel MS. How dihydrolipoamide dehydrogenase-binding protein binds dihydrolipoamide dehydrogenase in the human pyruvate dehydrogenase complex. The Journal of Biological Chemistry. 2006, 281 (1): 648–55. doi:10.1074/jbc.M507850200. PMID 16263718.
深入閱讀
- Silverberg MS, Cho JH, Rioux JD, et al.. [http//www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC2652837/ Ulcerative colitis-risk loci on chromosomes 1p36 and 12q15 found by genome-wide association study.]. Nat. Genet.. 2009, 41 (2): 216–20. doi:10.1038/ng.275. PMID 19122664. PMC 2652837.
- Scherer SW, Cheung J, MacDonald JR, et al.. [http//www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC2882961/ Human chromosome 7: DNA sequence and biology.]. Science. 2003, 300 (5620): 767–72. doi:10.1126/science.1083423. PMID 12690205. PMC 2882961.
- Brautigam CA, Chuang JL, Tomchick DR, et al.. Crystal structure of human dihydrolipoamide dehydrogenase: NAD+/NADH binding and the structural basis of disease-causing mutations.. J. Mol. Biol.. 2005, 350 (3): 543–52. doi:10.1016/j.jmb.2005.05.014. PMID 15946682.
- , Barrett JC, Lee JC, et al.. Genome-wide association study of ulcerative colitis identifies three new susceptibility loci, including the HNF4A region.. Nat. Genet.. 2009, 41 (12): 1330–4. doi:10.1038/ng.483. PMID 19915572.
- Reed LJ, Hackert ML. Structure-function relationships in dihydrolipoamide acyltransferases.. J. Biol. Chem.. 1990, 265 (16): 8971–4. PMID 2188967.
- Ciszak EM, Makal A, Hong YS, et al.. How dihydrolipoamide dehydrogenase-binding protein binds dihydrolipoamide dehydrogenase in the human pyruvate dehydrogenase complex.. J. Biol. Chem.. 2006, 281 (1): 648–55. doi:10.1074/jbc.M507850200. PMID 16263718.
- Asano K, Matsushita T, Umeno J, et al.. A genome-wide association study identifies three new susceptibility loci for ulcerative colitis in the Japanese population.. Nat. Genet.. 2009, 41 (12): 1325–9. doi:10.1038/ng.482. PMID 19915573.
- Odièvre MH, Chretien D, Munnich A, et al.. A novel mutation in the dihydrolipoamide dehydrogenase E3 subunit gene (DLD) resulting in an atypical form of alpha-ketoglutarate dehydrogenase deficiency.. Hum. Mutat.. 2005, 25 (3): 323–4. doi:10.1002/humu.9319. PMID 15712224.
- Brautigam CA, Wynn RM, Chuang JL, et al.. Structural insight into interactions between dihydrolipoamide dehydrogenase (E3) and E3 binding protein of human pyruvate dehydrogenase complex.. Structure. 2006, 14 (3): 611–21. doi:10.1016/j.str.2006.01.001. PMID 16442803.
- Kim H. Activity of human dihydrolipoamide dehydrogenase is largely reduced by mutation at isoleucine-51 to alanine.. J. Biochem. Mol. Biol.. 2006, 39 (2): 223–7. PMID 16584639.
- Sugden MC, Holness MJ. Recent advances in mechanisms regulating glucose oxidation at the level of the pyruvate dehydrogenase complex by PDKs.. Am. J. Physiol. Endocrinol. Metab.. 2003, 284 (5): E855-62. doi:10.1152/ajpendo.00526.2002. PMID 12676647.
- Wang YC, Wang ST, Li C, et al.. The role of amino acids T148 and R281 in human dihydrolipoamide dehydrogenase.. J. Biomed. Sci.. 2008, 15 (1): 37–46. doi:10.1007/s11373-007-9208-9. PMID 17960497.
- Brown AM, Gordon D, Lee H, et al.. Association of the dihydrolipoamide dehydrogenase gene with Alzheimer's disease in an Ashkenazi Jewish population.. Am. J. Med. Genet. B Neuropsychiatr. Genet.. 2004, 131B (1): 60–6. doi:10.1002/ajmg.b.30008. PMID 15389771.
- Babady NE, Pang YP, Elpeleg O, Isaya G. Cryptic proteolytic activity of dihydrolipoamide dehydrogenase.. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A.. 2007, 104 (15): 6158–63. doi:10.1073/pnas.0610618104. PMID 17404228.
- Wang YC, Wang ST, Li C, et al.. The role of N286 and D320 in the reaction mechanism of human dihydrolipoamide dehydrogenase (E3) center domain.. J. Biomed. Sci.. 2007, 14 (2): 203–10. doi:10.1007/s11373-006-9136-0. PMID 17171578.
- Foster LJ, Rudich A, Talior I, et al.. Insulin-dependent interactions of proteins with GLUT4 revealed through stable isotope labeling by amino acids in cell culture (SILAC).. J. Proteome Res.. 2006, 5 (1): 64–75. doi:10.1021/pr0502626. PMID 16396496.
- Kim H. Asparagine-473 residue is important to the efficient function of human dihydrolipoamide dehydrogenase.. J. Biochem. Mol. Biol.. 2005, 38 (2): 248–52. PMID 15826505.
- Hiromasa Y, Fujisawa T, Aso Y, Roche TE. Organization of the cores of the mammalian pyruvate dehydrogenase complex formed by E2 and E2 plus the E3-binding protein and their capacities to bind the E1 and E3 components.. J. Biol. Chem.. 2004, 279 (8): 6921–33. doi:10.1074/jbc.M308172200. PMID 14638692.
- Wynn RM, Kato M, Machius M, et al.. Molecular mechanism for regulation of the human mitochondrial branched-chain alpha-ketoacid dehydrogenase complex by phosphorylation.. Structure. 2004, 12 (12): 2185–96. doi:10.1016/j.str.2004.09.013. PMID 15576032.
- Martins-de-Souza D, Gattaz WF, Schmitt A, et al.. [http//www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC2684104/ Proteome analysis of schizophrenia patients Wernicke's area reveals an energy metabolism dysregulation.]. BMC Psychiatry. 2009, 9: 17. doi:10.1186/1471-244X-9-17. PMID 19405953. PMC 2684104.
外部連結
二氫硫辛醯胺脫氫酶引用了美國國家醫學圖書館提供的資料,這些資料屬於公共領域。
參考來源
更多醫學百科條目